Understanding the Side Effects of Antihistamines: What You Need to Know
Seasonal allergies can be frustrating. Sneezing, a runny nose, itchy eyes—it’s no surprise that millions of people reach for antihistamines to find relief. Antihistamines are a type of medicine that help block the effects of histamine, a chemical your body releases during allergic reactions. But like all medicines, antihistamines can have side effects.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the most common side effects of modern antihistamines—especially the ones you’re most likely to see on store shelves, such as cetirizine (Zyrtec®), fexofenadine (Allegra®), and loratadine (Claritin®). We’ll also give you practical tips to reduce side effects and help you make informed choices about allergy treatment.
What Are Antihistamines?
Antihistamines are medications that help reduce symptoms caused by allergic reactions. They are especially helpful for allergic rhinitis (commonly known as hay fever), hives, and other allergy-related conditions. There are two main types:
First-generation antihistamines (like diphenhydramine or Benadryl®): These are older drugs that often cause drowsiness and other side effects.
Second-generation antihistamines (like cetirizine, fexofenadine, and loratadine): These newer options are preferred by most doctors because they cause fewer side effects and don’t usually make you feel sleepy.
The American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology recommends second-generation antihistamines over first-generation ones due to their better safety profile and fewer central nervous system effects .
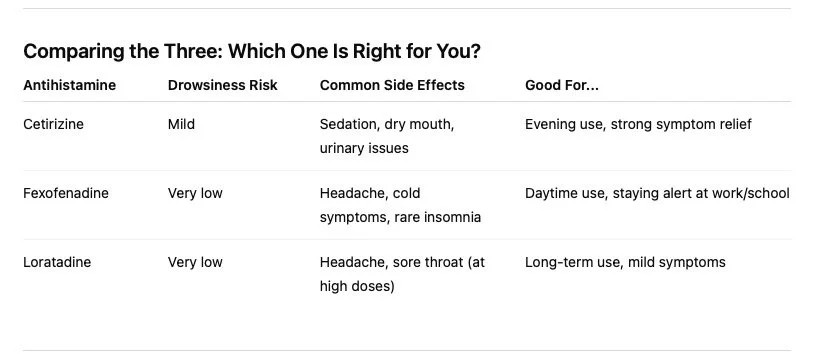
Cetirizine (Zyrtec®): Effective but May Cause Sleepiness
Cetirizine is a widely used second-generation antihistamine. It’s known for being fast-acting and effective at relieving allergy symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose.
Common Side Effects:
Drowsiness or mild sedation: Occurs in about 10% of people
Dry mouth or dry nasal passages
Urinary retention (trouble fully emptying the bladder), though this is rare
Even though cetirizine is less sedating than older antihistamines, it may still cause drowsiness in some users. This effect tends to be mild, but if you're sensitive, it might be noticeable.
Practical Tips:
Try taking cetirizine at night if it makes you drowsy.
Avoid alcohol or other sedating medications while using cetirizine.
Stay hydrated to help reduce dry mouth and nasal dryness.
Fexofenadine (Allegra®): Least Likely to Cause Drowsiness
Fexofenadine is another popular second-generation antihistamine that’s known for being non-drowsy. It works well for many people and is often recommended for those who need to stay alert during the day, such as students or workers.
Common Side Effects:
Headache (in about 10.6% of people)
Cold or flu-like symptoms (such as upper respiratory infections)
Back pain
Rare effects: insomnia, nervousness, and sleep disturbances
Most people tolerate fexofenadine very well, and many studies show its side effects are nearly the same as a placebo (sugar pill) .
Practical Tips:
If fexofenadine gives you a headache, try taking it with food and drink plenty of water.
Avoid taking it too late in the day if it affects your sleep, though this is rare.
Loratadine (Claritin®): Long-Lasting Relief with Minimal Side Effects
Loratadine is another non-drowsy antihistamine that works well for many allergy sufferers. It’s often taken once a day and starts working within 1 to 3 hours after taking it.
Common Side Effects:
Headache
Sore throat (pharyngitis)
Drowsiness (at higher than normal doses)
Loratadine is considered very safe, with a minimal effect on the brain and nervous system, which means it usually doesn’t make people feel tired or sluggish .
Practical Tips:
Stick to the recommended dose to avoid drowsiness.
Combine with a nasal saline spray if sore throat or dryness becomes both
Comparing Antihistamines